Featured Article

Electrophoresis is an analytical method frequently used in nucleic acid and protein analysis to separate macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins based on their size and charge. The technique is widely employed in the fields of medical diagnostics, life sciences, and clinical research.
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) systems separate nucleic acids and proteins with high accuracy and in a short period of time. CE separates molecules according to charge and size. The basic difference between capillary electrophoresis and gel electrophoresis is that, in CE, molecules are separated inside a small capillary tube filled with conductive buffer rather than gel. Separation of molecules using CE is faster and provides higher resolution because the thin tubes have a higher surface-to-volume ratio, which enables heat to dissipate faster and the system to run at high voltages without overheating. Moreover, CE requires only a small amount of sample, conserving rare and expensive samples.
While capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE) has been used for protein separation for more than two decades, current methods are becoming more robust and reliable for protein analysis, and some CGE methods have been used routinely for the analysis of protein-based pharmaceuticals and quality controls.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) has been used for size-based separations of proteins for over four decades and is still the workhorse for protein separations and analyses in most biological research laboratories. The basic procedure includes: 1) preparing a gel and assembling the gel apparatus; 2) mixing a protein sample with a buffer containing SDS and heating the mixture at an elevated temperature; 3) loading the SDS–protein mixture into the gel inside the gel apparatus and performing the electrophoresis; and 4) fixing, staining/destaining, and quantitating the separated proteins. If SDS is allowed to react with sample proteins completely, the reactions should produce SDS–protein complexes having similar charge densities (or mass-to-charge ratios). When these complexes are separated electrophoretically, their mobilities will be dependent on their sizes, with smaller proteins having greater mobilities. The mobility values decrease linearly with the logarithm of protein molecular masses, which is the basic separation principle of the technique. SDS-PAGE is time-consuming and labor-intensive. It is believed that many manual operations—e.g., gel preparation, sample loading, and staining/destaining—are sources of irreproducibility.
SDS-capillary gel electrophoresis (SDS-CGE), also called capillary sieving electrophoresis (CSE) or capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE), has many advantages over classical SDS-PAGE, including on-column detection, automated operation, greater resolving power, and accurate protein quantification and molecular weight determination.
CGE methodology/instrumentation
The basic apparatus for CGE is identical to that of capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) and consists of a capillary column, an on-column detector, and a high-voltage power supply. The major difference between the two techniques is the separation media: a sieving matrix is employed in CGE, while a background electrolyte solution is utilized in CZE.
The Qsep400 (BiOptic, Inc., New Taipei City, Taiwan) is an easy-to-use CGE system that integrates microcapillary electrophoretic technology into a plug-and-play disposable pen-shaped multicapillary gel cartridge (Figure 1) with automated liquid handling (96 samples) and real-time fluorescent detection and analysis. Optimized for high resolution and high throughput at ambient temperatures, the system provides improved peak resolution, good linear dynamic range, and reproducible migration times with a lowered instrument and sample analysis cost.
 Figure 1 – Qsep400 capillary gel electrophoresis instrument with four-channel gel cartridge.
Figure 1 – Qsep400 capillary gel electrophoresis instrument with four-channel gel cartridge.Materials and methods
• Instrument detection: Qsep400 (ex./em.: 465–485 nm/510–535 nm)
• Cartridge: P2 gel cartridge
• Sample treatment: sample dissolved in 1× dilution buffer and heated at 100 °C for 5 min
• Method: sample injection—4 kV for 5 sec; separation at 4 kV.
Operation is as follows: 1) Insert P2 gel cartridge and place samples, 2) select proper method, 3) click “run,” and 4) analyze results.
Results
CGE analysis
To evaluate suitability of the system, the protein standard and an unknown protein sample were separated by the multichannel cartridge. Samples were electrokinetically introduced at 4 kV for 5 sec and electrophoresis was performed at a constant voltage of 4 kV (Method: M-4-5-4kv).
An Invitrogen BenchMark protein size ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) containing recombinant proteins of 11, 21, 32, 40, 63, 98, and 155 kDa was used to assist in the gel formulation phase to optimize the resolving capacity of the gel and to estimate the molecular weight (MW) of unknowns (Figure 2). In addition, the platform was adopted for evaluating the purity and heterogeneity of sheep immunoglobulins (IgGs) for 10 sec (Figure 3) and analyzed the composition of heavy-chain and light-chain IgGs.
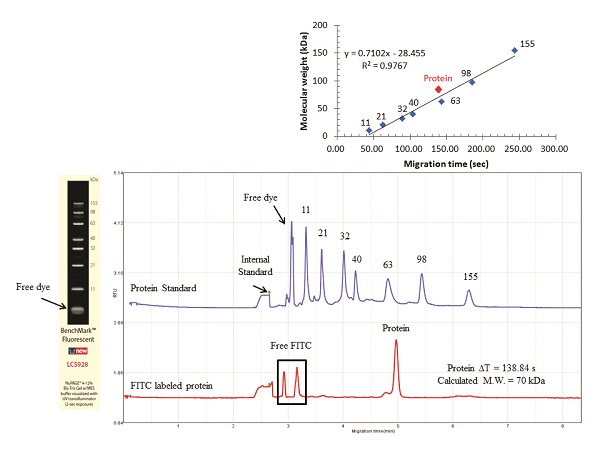 Figure 2 – Protein standard separation and MW determination of an unknown sample using the multichannel cartridge. Samples were introduced electrokinetically at 4 kV for 5 sec and electrophoresis was performed at constant voltage of 4 kV.
Figure 2 – Protein standard separation and MW determination of an unknown sample using the multichannel cartridge. Samples were introduced electrokinetically at 4 kV for 5 sec and electrophoresis was performed at constant voltage of 4 kV.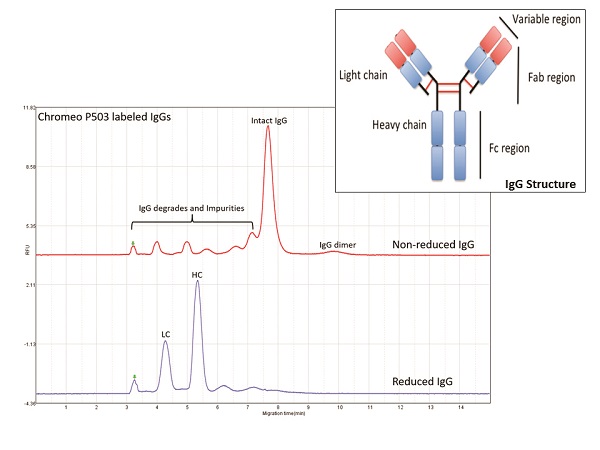 Figure 3 – Biochemical characterization of sheep IgGs. Samples labeled with Sigma-Aldrich Chromeo P503 (MilliporeSigma, Billerica, MA) were treated with or without reducing agent. Samples were introduced electrokinetically at 4 kV for 10 sec and separated at a constant voltage of 4 kV.
Figure 3 – Biochemical characterization of sheep IgGs. Samples labeled with Sigma-Aldrich Chromeo P503 (MilliporeSigma, Billerica, MA) were treated with or without reducing agent. Samples were introduced electrokinetically at 4 kV for 10 sec and separated at a constant voltage of 4 kV.Conclusion
The Qsep400 multicapillary system is a high-quality control platform that provides the simplest solution for fluorescent analysis of proteins. Compared to UV detection, system sensitivity was improved, and will be further optimized to achieve the sensitivity levels of a silver stain SDS-PAGE assay. With the ready-to-use gel cartridge, users can set up the instrument in 1 minute and attain results within 3–7 minutes (96 samples in ~1.5 hr). The data can also be released by batch or individually with fully detailed information.
Dawn Lin, Yi-Wen Yuan, Ming-Jhy Hseu, and Eric Tsai are with BiOptic, Inc., New Taipei City, Taiwan (ROC). Varouj Amirkhanian is with BiOptic, Inc., 1409½ Foothill Blvd., La Canada Flintridge, CA 91011, U.S.A.; tel.: 818-679-4413; e-mail: [email protected]; www.bioptic.com.tw